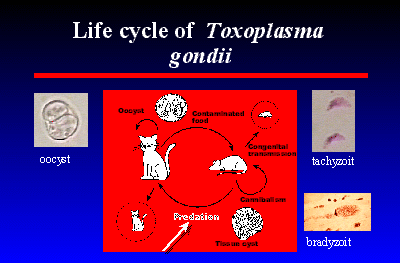
Life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii


A classical model for studying the manipulation hypothesis is also the protozoon T. gondii. This heteroxenous coccidium needs to get from its intermediate host (usually rodent) into its definitive host, the cat. It has been known for a long time that the Toxoplasma induces many changes in the behavior of its intermediate hosts that can be considered adaptive in the sense that they increase the probability of the transmission of the parasite from intermediate into definitive host by predation.